Reviewed by Doctor Balldin
ACL injuries are among the most common and debilitating injuries for athletes and active individuals. The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) plays a vital role in maintaining knee stability, allowing for proper movement and agility. When this ligament is injured, it can significantly impact one’s ability to participate in sports and daily activities. Understanding the different types of ACL injuries, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options, such as arthroscopy with ligament reconstruction/repair and physical therapy, is essential for anyone looking to stay active and healthy. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of ACL injuries, helping you recognize, treat, and prevent them effectively.
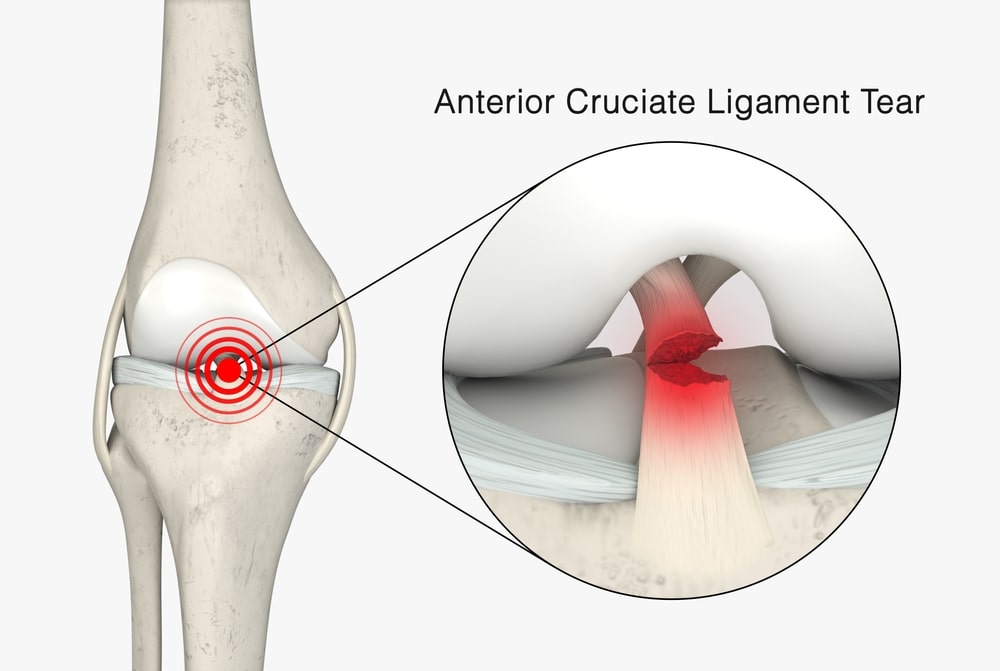
What is an ACL injury?
An ACL injury is a much to common knee injury, especially for athletes. The ACL is one of the major stabilizing ligaments in your knee and is crucial for rotation and side to side activities of the joint. Injuries occur when the ligament is stretched or torn, often during activities that involve sudden stops, jumps, or changes in direction. Most ACL injuries that occur are non-contact injuries.Types of ACL Injuries
Understanding the various types of ACL injuries is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Here are the primary types of ACL injuries:Complete Tear
A complete tear occurs when the ACL is entirely torn, leading to significant knee instability. Most often it requires surgical intervention and a lengthy rehabilitation process.Partial Tear
Only a portion of the ACL is damaged in a partial tear. However, a partial tear can still cause instability and may require medical attention. Partial tears might heal with conservative treatment, but sometimes surgery is necessary. It is crucial to see a doctor to learn how to prevent a partial tear from becoming a complete tear.Avulsion
An avulsion occurs when the ligament is torn away from the bone or the ACL along with a piece of the born is torn. This type of injury is less common but can be severe. It often requires surgical repair to reattach the ligament or the piece of the bone avulsed back to its native location..Causes of ACL Injuries
ACL injuries typically result from:- Sudden stops of changes in direction: These movements put excessive stress on the knee.
- Jumping and landing awkwardly: Incorrect landing techniques can strain or tear the ACL.
- Direct impact to the knee: Contact sports or accidents can lead to ACL injuries.
- Overuse from repetitive stress on the knee: Activities that involve frequent knee bending and twisting can cause wear and tear over time.
Symptoms of an ACL Injury
Recognizing the symptoms of an ACL injury is the key to early intervention. Common symptoms include:- A loud pop at the time of injury: Many individuals report hearing and feeling a popping sound when the injury occurs.
- Severe pain and inability to continue activities: Pain is often immediate and intense, preventing further movement but it does not have to be severe.
- Rapid swelling: Swelling usually occurs within a few hours of the injury.
- Loss of range of motion: The knee may become stiff and difficult to move.
- Instability or “giving way” of the knee: The knee may feel unstable or buckle under weight.
How To Treat an ACL Injury
Treating an ACL injury effectively requires a combination of immediate first aid, professional medical evaluation, and long-term rehabilitation. Here are the primary treatment options:Immediate First Aid
Initial treatment often involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) to reduce pain and swelling. This approach helps manage symptoms and prevent further damage.Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation exercises help restore knee strength and function. Physical therapy is crucial for recovery, whether surgery is required or not. A physical therapist will design a personalized exercise program to improve mobility, strength, and stability.Surgical Options
In severe cases, especially for athletes, surgery may be necessary to reconstruct the torn ligament. Procedures like knee arthroscopy along with ACL reconstruction can be highly effective. Surgery is often followed by an extensive rehabilitation program to ensure full recovery of 9-12 months. Read about the Do’s and Don’t After ACL Surgery for post-surgery care.How To Prevent ACL Injury
Preventing ACL injuries involves a proactive approach to strengthening the knee, improving flexibility, and using proper techniques during physical activities. Here are some effective prevention tips:Strength Training
Regular leg strength training can enhance muscle balance and knee stability. Focus on exercises that target the glutes, quadriceps, hamstrings, and core muscles.Proper Technique
Learning and maintaining proper techniques during sports and physical activities can reduce the risk of injury. Coaches and trainers can provide guidance on the correct form and movements.ACL Injury Prevention Programs
Following scientifically studied ACL injury prevention programs and incorporating them into weekly training sessions have been shown to decrease the injury rate as long as the programs are kept up.When To Seek a Doctor for an ACL Tear
If you suspect an ACL injury, seeking medical attention promptly is important. Signs that you should see a doctor include:- Persistent knee pain and swelling.
- Inability to bend or straighten the knee.
- Instability when walking.
- Inability to bear weight.