Ankle
Replacement Center
When To Consider Ankle Replacement
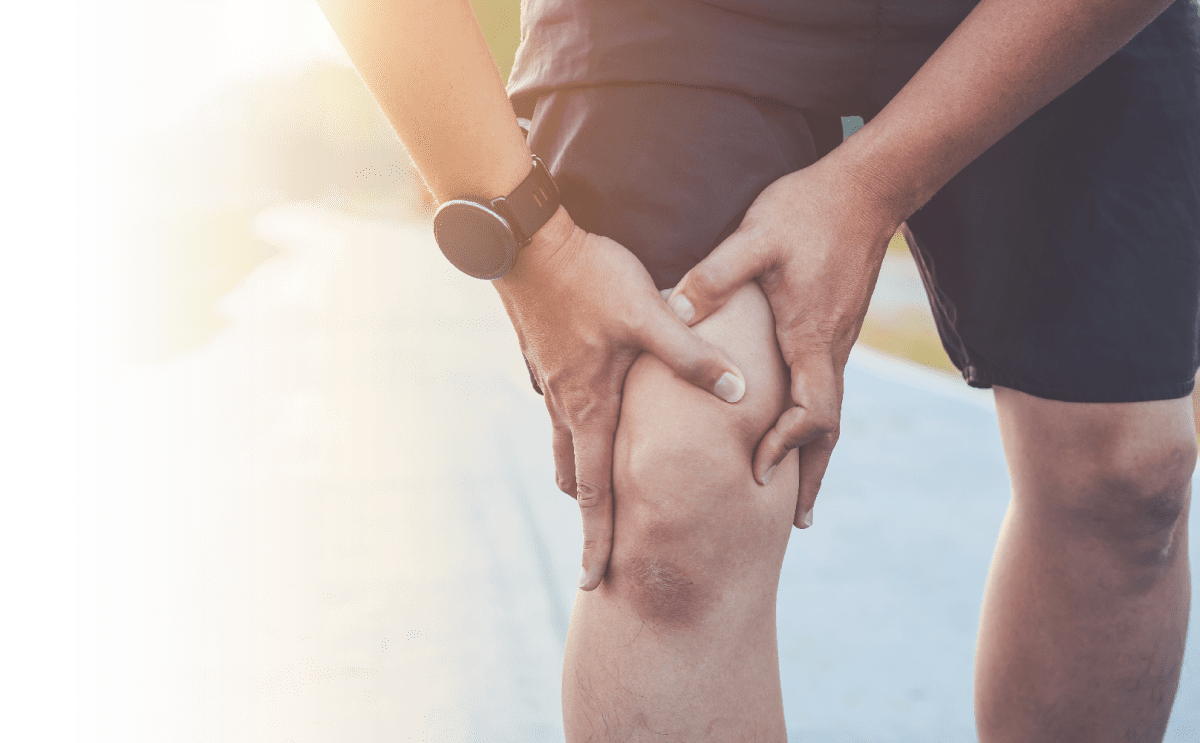
Though less common than some other joint replacement procedures, total ankle replacement has the same goal: to increase mobility and alleviate joint pain due to arthritis.
It may be time for you to consider a total ankle replacement if:
- You have intense ankle pain that keeps you awake at night or wakes you up.
- You have ankle pain that limits your daily activities, like standing, walking, or climbing stairs.
- You have noticed weakness and/or decreased range of motion in your ankle.
- You have tried conservative treatment options for ankle pain with no success.
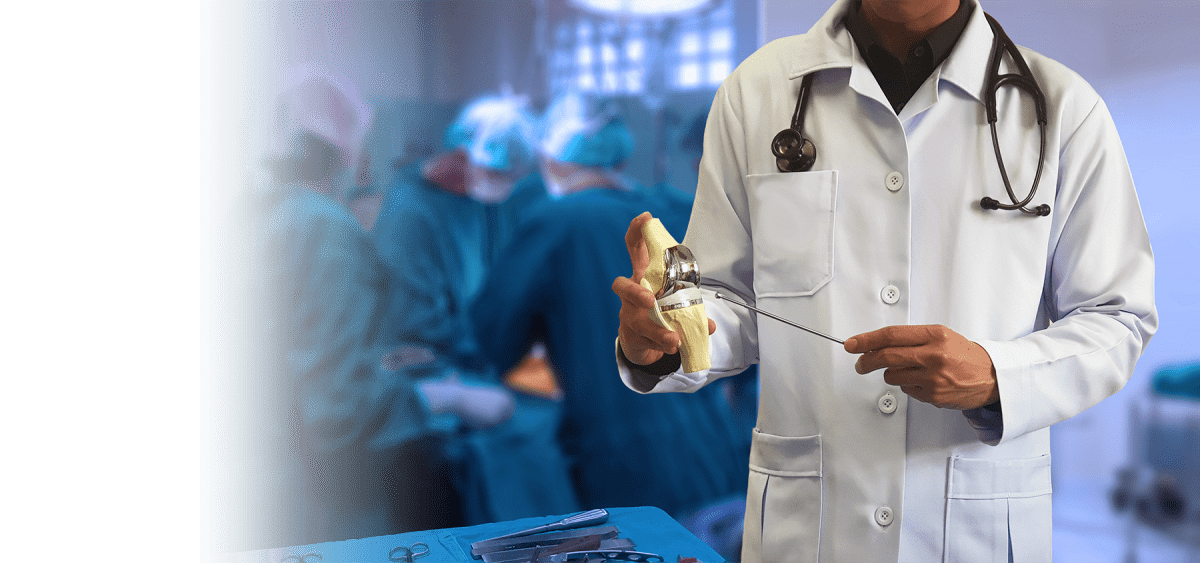
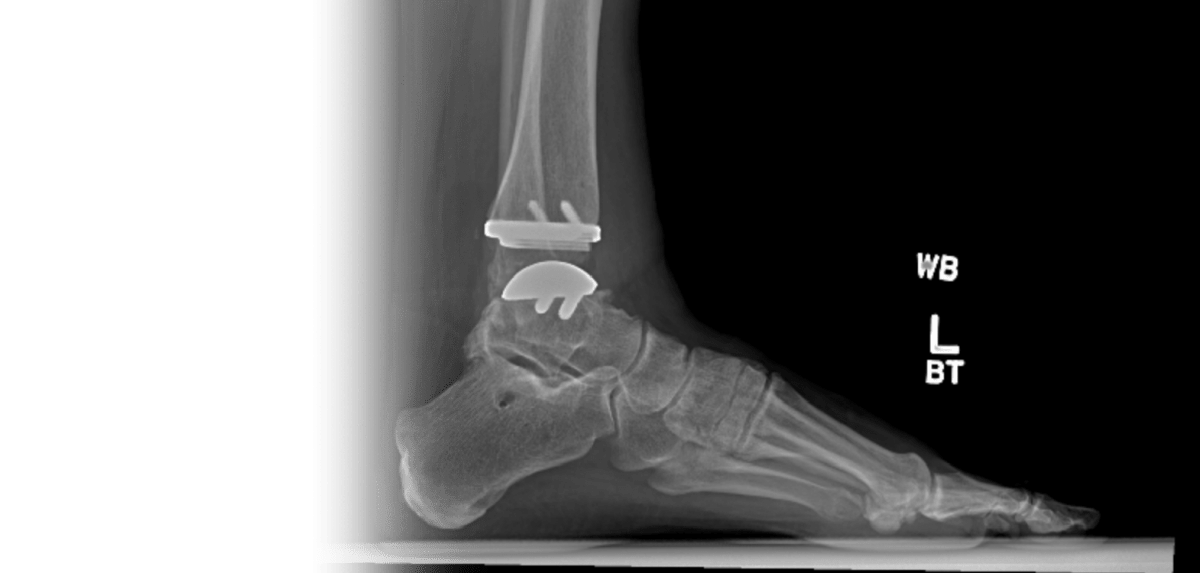
When the articular cartilage surrounding your ankle joint (where the tibia meets the talus) is damaged beyond repair, most often due to arthritis that has occurred as a result of the previous injury to the ankle joint, ankle replacement surgery seeks to remove the damaged portion of the ankle joint and replace it with an artificial component to increase range of motion and alleviate ankle pain.
Total Ankle Replacement
A total ankle replacement (or total ankle arthroplasty) involves 5 main steps:
- Preparation of the Tibia – The damaged cartilage, as well as a small amount of the bone, is removed from the bottom of your shin bone (tibia) and the new surface is shaped to fit the designated implant.
- Preparation of the Talus – The damaged cartilage, as well as a small amount of the bone, is removed from the top of your ankle bone (talus) and the new surface is shaped to fit the designated implant.
- Positioning of Tibia Implant – A metal implant is positioned on the cut end of the tibia and cemented into place.
- Positioning of Talus Implant – A metal implant is positioned on the cut end of the talus and cemented into place.
- Spacing – A plastic spacer is inserted between the two metal implants to provide a smooth gliding surface, acting in place of cartilage for the artificial ankle.
The bottom line is that ankle replacement surgery is a last resort for dealing with arthritic ankle pain. However, if you have tried conservative treatment options with no success and persistent ankle pain is interfering with your life and limiting your daily activities, it is time to talk with your doctor about an ankle replacement.
Your Ankle Replacement Team
Book an Appointment
FIND A LOCATION

Mission Trail Medical Plaza
3327 Research Plaza, #215
San Antonio, TX 78235

Christus Santa Rosa NW, Tower I
2829 Babcock Rd., #700
San Antonio, TX 78229

Ridgewood Orthopaedic Center
19138 US-281 N
San Antonio, TX 78258
PHYSICIANS: Linzy Fitzsimons, M.D. , Scott R. Seidel, D.C. , B. Christian Balldin, M.D. , Richard Nauert, M.D. , Jessica F. Rutstein, D.P.M. , Sergio Viroslav, M.D. , Dustin B. Rinehart, M.D. , Randall C. Marx, M.D. , Justin Robbins, M.D. , Patrick Ahern, M.D. , Joseph Poku, M.D. , Eloy Ochoa, Jr., M.D. , M. Brandon Dobson, M.D. , David E. Vizurraga, M.D. , David T. Hughes, D.P.M. , Jonathan S. Duncan, M.D. , Lauren E. Karbach, M.D. , Michaelia Sunderland, M.D. , Bryan W. Kaiser, M.D. , Richard L. Ursone, M.D. , David R. Espinoza, M.D. , Robert U. Hartzler, M.D., M.S. , Matthew C. Swann, M.D. , Cory J. Moczygemba, DPM , Casey D. Taber, M.D. , Ephraim K. Brenman, D.O., R.M.S.K. , Stephen C. Drukker, M.D. , Alexander S. Rowland, M.D. , G. Lane Naugher, M.D.

Westover Hills Medical Plaza I
11212 State Hwy 151, #150
San Antonio, TX 78251

Grayson Heights
1422 East Grayson Street, Ste 102
San Antonio, TX 78208
PHYSICIANS: S. Josh Bell, M.D. , Mickey S. Cho, M.D.

The Orthopaedic Institute
400 Concord Plaza Dr.
San Antonio, TX 78216
PHYSICIANS: G. Lane Naugher, M.D. , Eduardo Moreno, M.D. , Casey D. Taber, M.D. , Shane C. Eizember, M.D. , Matthew C. Swann, M.D. , Lauren E. Karbach, M.D. , Christopher J. Tucker, M.D. , Randall C. Marx, M.D. , David R. Espinoza, M.D. , S. Josh Bell, M.D. , Stephen T. Gates, M.D. , Frank J. Garcia, M.D. , Alexander S. Rowland, M.D. , David E. Vizurraga, M.D. , Charles E. Bryant, M.D. , Eloy Ochoa, Jr., M.D. , Anthony Montanez, M.D. , Ephraim K. Brenman, D.O., R.M.S.K. , Christian A. Woodbury, M.D. , Justin Robbins, M.D. , B. Christian Balldin, M.D.

Resolute Retail Plaza
601 Creekside Crossing #106
New Braunfels, TX 78130

Schertz Parkway Professional Plaza
5000 Schertz Parkway, #600
Schertz, TX 78154
PHYSICIANS: Jonathan S. Duncan, M.D. , Charles E. Bryant, M.D. , Michaelia Sunderland, M.D. , Nicholas Nira, D.C. , Richard L. Ursone, M.D. , Richard Nauert, M.D. , Jeffrey B. Shroff, M.D. , Dustin B. Rinehart, M.D. , Mickey S. Cho, M.D. , Lauren E. Karbach, M.D. , Justin Robbins, M.D. , Emmanuel C. Nwelue, Jr., M.D.
Quarry Area
Add an optional description to your map pin
Ridgewood Orthopaedic Center
Schertz
Medical Center
Westover Hills
WorkSmart at Grayson Heights
Brooks City Base
New Braunfels